Ceramic and Metal Foams
Ceramic and Metal Foam Applications
- Energy storage devices
- Heat sinks and heat exchangers
- High temperature insulation
- Filled with carbon/phenolic (ablating)
- Biomedical devices
- Core for lightweight, high stiffness sandwich panel
- Furnace fixturing and tooling
- Molten metal filtration
- Noise reduction
- Lightweight mirrors
- Fuel vaporizers/injectors
- Hot gas filters
- Catalyst supports
- Lightweight armor
- Rocket engines
Ceramic and Metal Foam Advantages
- Resistant to thermal shock
- High specific stiffness
- High surface area
- Low pressure drop
- Tailorable pore size and foam density
- Ability to apply solid ceramic or metal facesheets to create actively cooled structures
- Fabrication from various ceramics and metals
Virtually any material that can be deposited by chemical vapor deposition can be used to infiltrate a foam and coat the ligaments. Once the coating fills ~5% of the original pore space, the mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of the whole are dominated by the properties of the coating.
Among the materials that can be deposited are pyrolytic carbon or graphite, refractory metals (e.g. niobium, tantalum, tungsten, molybdenum, and rhenium), and ceramic compounds (e.g. the oxides, nitrides, carbides, borides, and silicides of the metals).
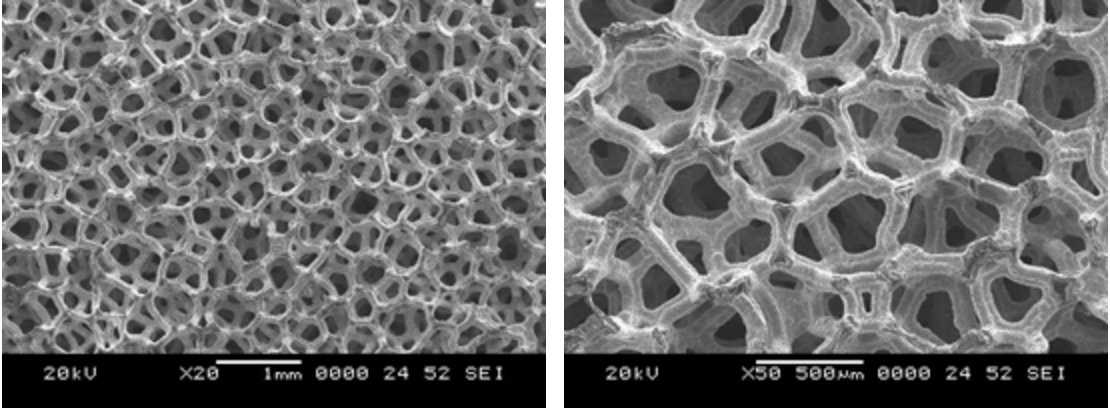
Open-cell silicon carbide foam showing uniform pore structure
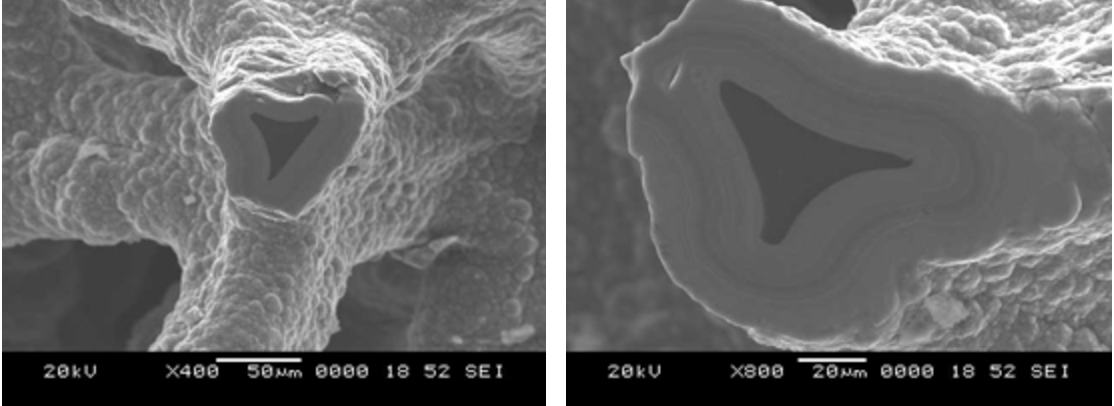

Individual foam ligaments showing uniform silicon carbide coating (gray areas) over carbon core (black triangular areas)
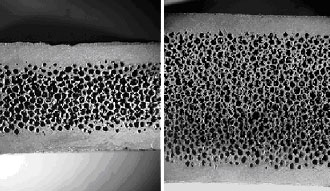
Foam-core sandwich structure in which fully dense silicon carbide facesheets are integrally bonded to 80-90 vol% porous, open-cell silicon carbide foam (both 5x). Refractory metal foam/facesheet structures are also feasible.
