Properties of Foam Materials
Abundant data on various foam materials offered by Ultramet are available on request. Selected information follows.
Reticulated Vitreous Carbon Foam
Typical Physical Properties of Open-Cell Reticulated Vitreous Carbon
| Pore sizes available | 10, 20, 30, 45, 65, 80, and 100 ppi |
| Ash content | 0.39 wt% at 1000°C |
| Bulk density | 0.045 g/cm3 |
| Ligament density | 1.538 g/cm3 |
| Resistivity | 0.75 Ω · cm |
| Specific heat | 0.30 cal/g/°C |
| Maximum use temperature | 350°C in air 3500°C inert |
| Thermal expansion, ppm/°C | |
| 0–200°C 0–500°C 0–1000°C |
1.15 1.65 1.65 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/m · K | |
| at 200°C at 300°C at 400°C at 500°C at 650°C at 800°C at 950°C |
0.085 0.125 0.180 0.252 0.407 0.625 0.882 |
| Compressive strength, kPa at 20°C | 625 (10% deflection) 763 (ultimate) |
| Compressive strength, kPa at 1000°C in argon | 391 (10% deflection) 628 (ultimate) |
| Shear strength at 20°C | 290 kPa |
| Tensile strength at 20°C | 690 kPa |
| Flexural strength at 20°C | 690 kPa |
| Flexural modulus | 58.6 MPa |
Silicon Carbide Foam
Typical Physical Properties of Open-Cell Silicon Carbide
| Pore sizes available | 10, 20, 30, 45, 65, 80, and 100 ppi |
| Bulk density | 0.16–1.28 g/cm3 |
| Relative density | 5–40% |
| Theoretical ligament density | 3.2 g/cm3 |
| Specific heat (10% SiC) | 0.34 cal/g/°C |
| Maximum use temperature | 1650°C in air 2500°C inert |
| Thermal expansion | see below |
| Thermal conductivity | see below |
| Strength | see below |
| Young’s modulus | see below |
| Strain to failure | 0.07% at 20°C |
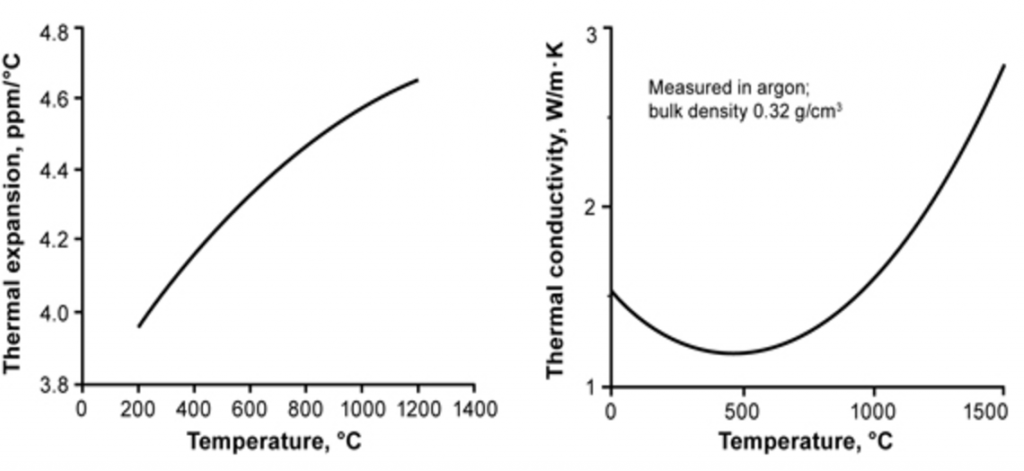
Thermal properties of silicon carbide foam produced to 10 vol% dense (0.32 g/cm3). Thermal expansion is independent of vol% density and matches that of solid silicon carbide.
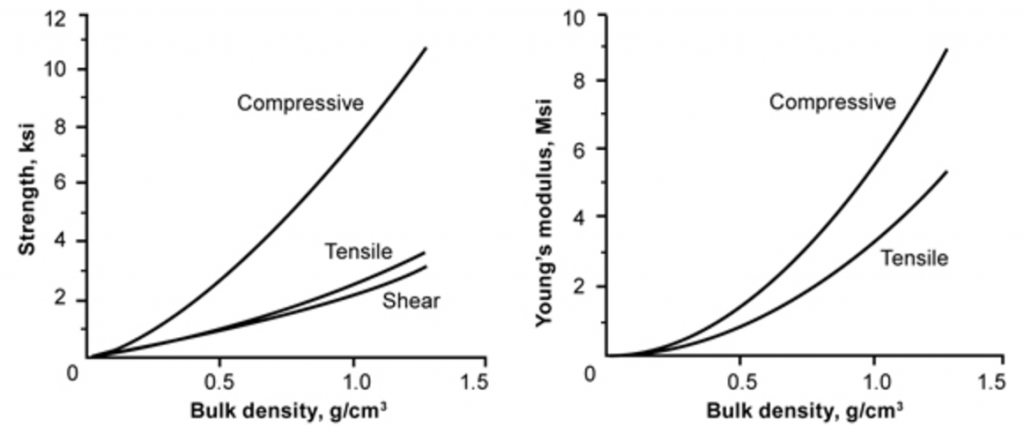
Strength and Young’s modulus as a function of bulk density for open-cell silicon carbide foam
Pressure drop data for water flow through 2 × 3 × ½” slabs of silicon carbide foam with water flowing parallel to the long axis of the sample; 80- and 100-ppi foams with relative densities of 20 and 30% were tested.
