Fiber Interface Coatings
Fiber interface coatings are critical to any fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composite system. Ultramet has unique capabilities to deposit proven interface coatings of oxides, nitrides, and carbides by ultraviolet-activated chemical vapor deposition either in single or multiple layers.
Ultraviolet-Activated Chemical Vapor Deposition
In a powerful variant of chemical vapor deposition, ultraviolet light rather than a conventional heat source promotes the chemical reaction in ultraviolet-activated chemical vapor deposition (UVCVD). In addition to fiber interface coatings, UVCVD is used to fabricate environmental and thermal barrier coatings.
How UVCVD Works
UVCVD is identical to CVD except that precursor gas reactants are activated to a more reactive state by exposure to ultraviolet light rather than a conventional heat source.
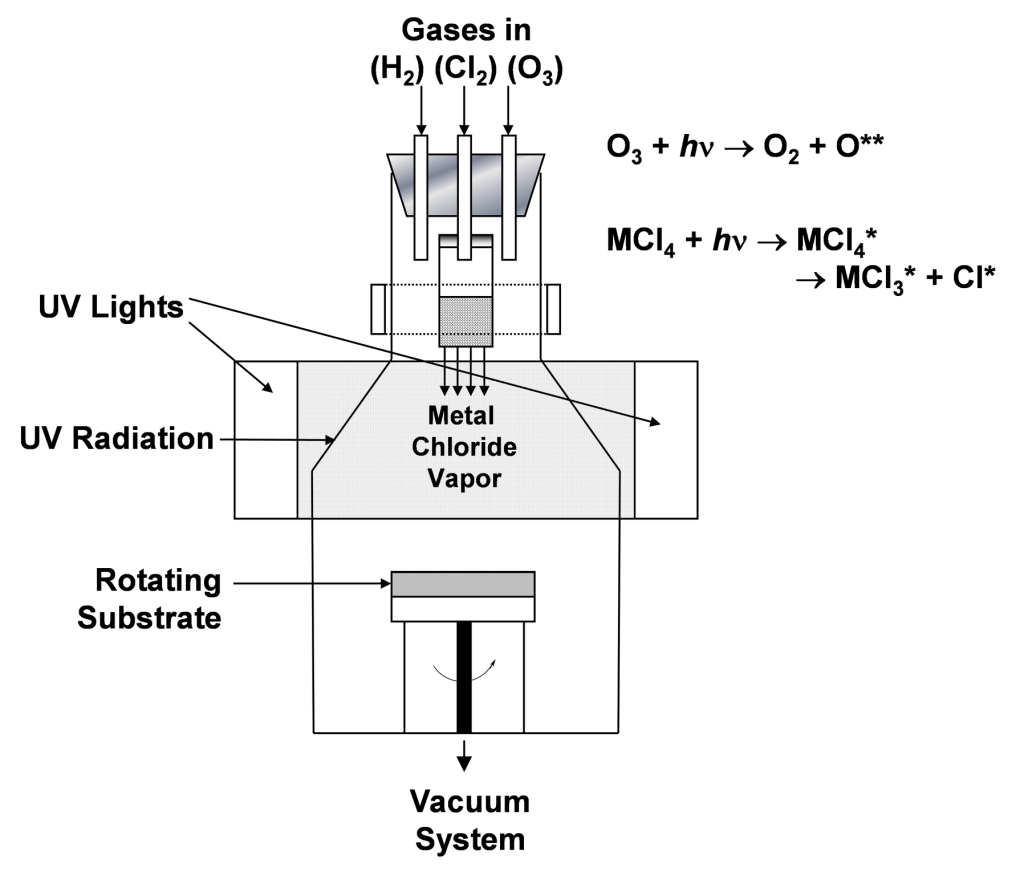
Advantages of UVCVD
- Deposition at room or low temperatures (<300ºC)
- Heating of substrate not required
- Minimal degradation of substrates
- Ability to deposit oxides onto substrates (e.g. carbon fibers) that are otherwise susceptible to an oxygen-containing environment at elevated temperatures
- Ability to apply to thick-section preforms and cavities within substrate materials, because process is not line-of-sight
- Uniform application of fiber interface coatings on fibers/fabrics/preforms
- Effective removal of oxides from metallic substrates without heating
- Thick, continuous deposits even in ultraviolet-blind regions
- Multiple layers that protect fibers and allow slip
Materials Deposited by UVCVD
Oxide and nitride interface coatings for carbon/silicon carbide/alumina fibers, fabrics, and woven preforms
| Oxide interface coatings for carbon/silicon carbide/alumina fibers, fabrics, and woven preforms | |
|---|---|
| Oxide coatings | Nonoxide coatings |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) Yttria-stablized zirconia (YSZ) Titania (TiO2) Alumina (AI2O3) Hafnia (HfO2) Yttria (Y203) Silica (SiO2) Tantala(Ta2O5) |
Pure metals: rhenium, tungsten Carbon Carbides: Silicon Carbide (SiC) Nitrides Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) Hafnium Nitride (HfN) Boron Nitride (BN) Silicon-doped BN (Si-BN) |
